Services
Electro-Polishing

Chemical Treatment of Stainless Steel Surface
Food equipment manufacturers and users choose stainless steels as the predominant materials of construction because of their excellent mechanical properties (e.g.: strength, formability, ductility and weldability) combined with a high level of corrosion resistance and cleanability. The latter two attributes, which are the primary determinants of the material's hygienic behaviour, rely upon the 'passive layer', a chromium- rich oxide film which naturally forms on all stainless steels. This layer is adequately protective for the vast majority of food and beverage applications.For higher demanding applications, the strength of the passive layer (and therefore the corrosion resistance) of the surface, can be improved by chemical passivation. The hygienic quality of the surface can be even further enhanced by electro-polishing to optimize topography, morphology and energy level.
Electropolishing is for effecting a lasting improvement of significant functional (surface)-properties of components made of different metallic alloys. Especially with components made of austenitic stainless steel alloys, not only the corrosion resistance can be improved substantially and sustainably by electropolishing which optimises the passive layer formation on the surface but also the cleaning behaviour due to a micro- smoothening of the surface.
A significant advantage of electropolishing is the creation of very smooth surfaces (typically Ra < 0.2 µm). The smoothing of the surface by means of electropolishing is demonstrated in Fig. 7. Moreover, metallically clean surfaces are created by electropolishing.
In comparison with other treatment procedures, the formation of optimal passive layers of austenitic stainless steels regarding Cr/Fe-relation and passive layer thickness for maximum corrosion resistance can be achieved.
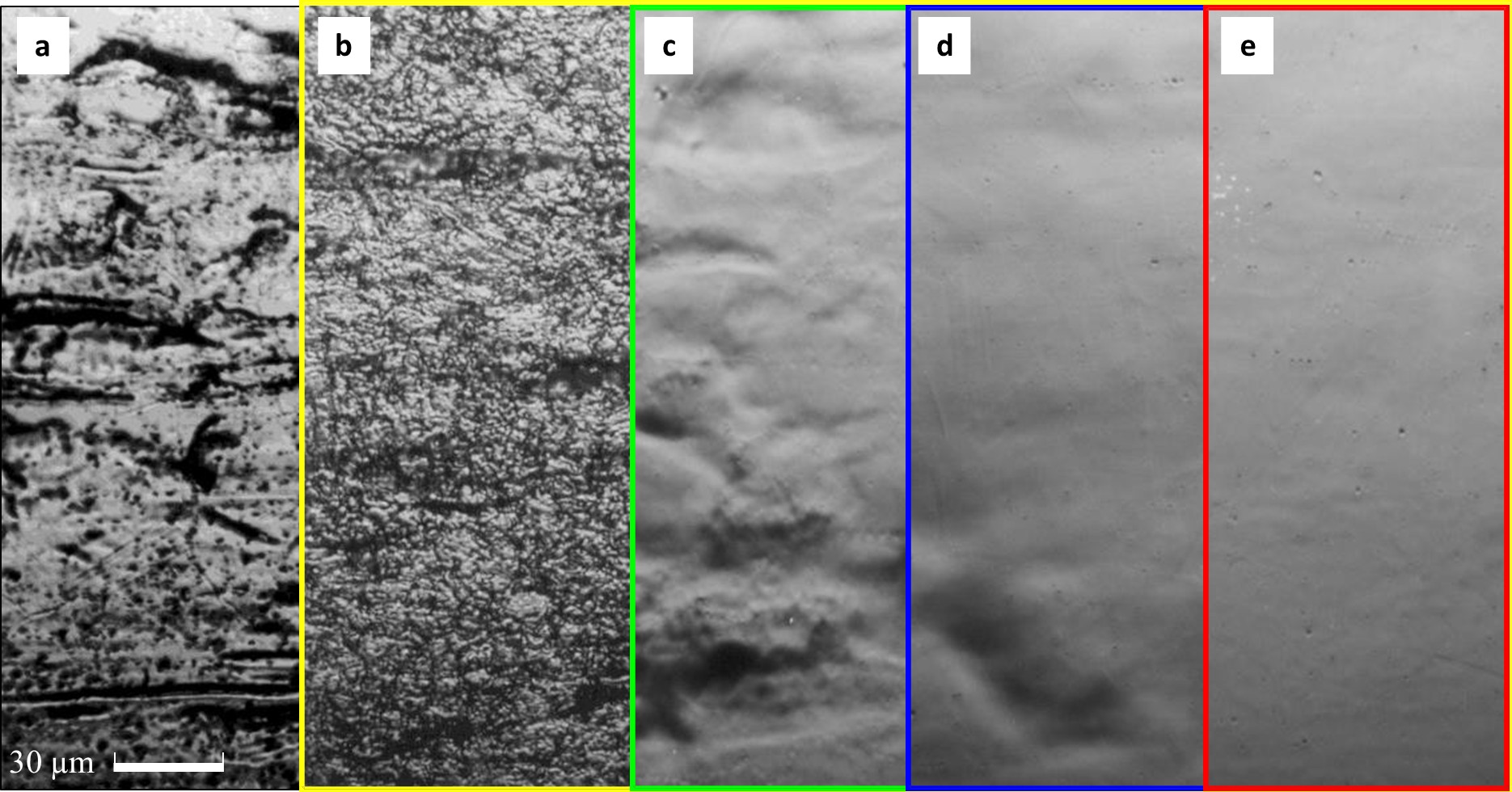
Electropolishing is effective in removing microroughness.
A schematic representation of the profile of a metal surface before and after electropolishiing is shown in Fig 1.
Electropolishing principles and set-up
During electropolishing, anodic dissolution of metal ions takes place in a suitable electrolyte using an external direct current source. Normally, phosphoric and sulphuric acid electrolytes are used for electropolishing austenitic stainless steels. The principal of the electropolishing set-up is illustrated in Fig. 6.&
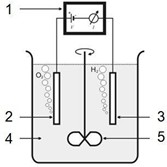
1 = Rectifier
2 = Anode: the positive pole of the rectifier.
This will be the stainless steel component
3 = Cathode: the negative pole of the rectifier.
This is made of copper (Cu).
4 = Electrolyte (phosphoric acid H3PO4 + sulphuric acid H2SO4 + additives) at approximately 50ºC
5 = Agitator (stirrer).
Setup for austenitic steel electropolishing (Source: EHEDG Doc.18)
RIGHTER electro-polishing of stainless steel items is compliant to ASME BPE requirements
The high surface quality is the result of years of experiences and know-how in processing electro-polishing. Significant process parameters are observed :
- Operating temperature of the electrolyte solution.
- The amplitude of the cathodes and their location relevant to the product.
- ph value of the solution.
- Processing duration that the part is immersed in the solution.
As a result, RIGHTER products stand out from competing products in the following ways:
A thicker EP layer to minimize rouging
Higher Chrome concentration for better corrosion resistance
Guaranteed smoothness (Ra) in all internal surfaces to reduce Bio film
